2026 Author: Leah Sherlock | sherlock@quilt-patterns.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 17:46:24
What is a gramophone record, in our time, perhaps, only those who were born in the USSR know. For the rest, it is something insignificant and forgotten. But at one time they were very popular. It was prestigious to have a record library at home. In addition, it was with them that the evolution of analog storage media began. Still, it's worth going a little deeper into the past and finding out all the details.

Features
It's much more common today to have CDs at home. But even they are already gradually going out of fashion. A gramophone record looks like a circle, on the sides of which there are continuous spiral grooves - tracks. The shape of the groove is modeled only by a sound wave, and it is thanks to it that the sound goes.
Special devices were used to read such media. Initially, these were gramophones, and then, already at the end of the era of records, special players appeared. If the CD moves very fast during reading, then the speed of gramophone sound carriers is equal to the speed of sound playback. For example, when there were gramophones and gramophones, soundretrieved by scrolling the handle. If you increase the scroll speed, then the sound speeds up.
Pros and cons
The main advantage of a gramophone record could be called the following factors:
- a kind of immunity to magnetic and electric fields;
- relatively high sound quality considering the time frame in which records were popular;
- Cheap method of mass production - hot pressing.
This historically important thing did not do without minuses:
- Temperature changes were dangerous for the material from which the records were made.
- Susceptibility to structure distortion in high humidity.
- The appearance of scratches for this kind of sound medium was fatal.
- Still, their sound is not perfect, gramophone records are noisy, especially when damaged.
- Loss of sound quality after prolonged use. In simple terms, wear.
All of the above minuses still outweighed the pros, the inventors began to look for new ways to record sound and more reliable media. Over time, compact discs were invented, but among their disadvantages was one, the most significant - the inevitable appearance of scratches.

How it works
Apparatus for reproducing sound changed, but the principle of extracting sound from gramophone records remained the same. It's all about the needle, which was present in all the players. She moves along the pathwhose form is constantly changing and fluctuating. The vibrations are gradually transferred to the membrane, it is she who is responsible for sound transmission.

If the player was electric, then there was no membrane - the vibrations of the needle were read by means of a transducer of mechanical vibrations, and from there they were transmitted to the amplifier. That's how gramophone records worked.
History
Of course, such players and media were not the first to be invented, they were preceded by many scientific achievements and several invented devices. The progenitor of the record known in the modern world can be considered a simple music box. But not everyone knows that there were several types of boxes.
Gramophone records include those in which a metal disk with an uneven and deep spiral groove was used to reproduce sound. This type of box also had a needle, which slid along the groove and read the full sequence of points, transmitting vibrations to the membrane. The principle of reproduction was the same as on the gramophone, the only exception was that the sound from the records was more professional. Not only the melody was recorded in the red, but also the voice, even several, for example, choral singing.
Development
Initially, serial pre-revolutionary gramophone records were small, only 175 millimeters in diameter, they were simply called seven-inch. This standard appeared at the end of the 19th century, in the 90s. Initially, the speed of the gramophone record was high, and the width of the track was incomparable with future morepractical products. They could only play 2 minutes of recording and only on one side.

Only at the beginning of the 20th century, namely in 1903, they became bilateral. The first to think of creating such a device were employees of the Odeon gramophone records factory. And after their developments, in the same year, records with a diameter of 300 millimeters were invented, which also increased the playing time. During this decade, only the works of the classics were recorded on media. They fit only 5 minutes of real-time music. There were four changes in plate size in total, two of which have already been mentioned. The most popular of all formats was 250mm media, already holding 1.5 times more sound than 7 media.
Records in the USSR

For a very long time in Soviet times, eight-inch gramophone records with an actual diameter of 185 millimeters were popular. This lasted until the mid-60s of the XX century, then the production of conventional (gramophone) media was curtailed, and new, more advanced, "tailored" for playback from electronic readers appeared on the market. Soviet gramophone records were completely replaced with newer ones, eight-inch records were left only for recording children's fairy tales and songs.
What now?
Despite the large-scale use of records by the Soviet people, they were still supplanted by smaller CDs. But citizens use gramophone carriersThe USSR continued until perestroika. Nowadays, vinyl LPs are not widely used anywhere, you can see them:
- During the work of the DJ and experiments in the field of sound processing.
- In the collection of an audiophile (a person who is a fan of this type of recording).
- At a collector's and antique shop.
- In other cases, they are simply stored on the shelves as a memory. Of course, there are those who sometimes play the record through the player, but only to remember the past times.
Despite the narrow specialization, such carriers are also used in the star industry. Famous artists record anniversary albums or just their own music on them.

Records in the 21st century
Morally and from a technical point of view, such media are outdated, they can not be bought everywhere, and not everyone can listen to them. Despite this, some people still gravitate toward records. Experts believe that this choice of sound is not due to the technical characteristics of the media. Someone thinks that the sound of gramophone records is warmer, livelier and better conveys the mood. Some people like to be nostalgic. There are few such people, but they still exist.
The psychological factor also plays a big role. Initially, all significant albums and music tracks were released on records. In this regard, people still think that having vinyl media in their collection is prestigious and fashionable.

Smallreleasing records is another psychological factor. Young people, and not only, are drawn to everything rare and small in number. It's kind of a way to show your personality. In this case, mass production is contraindicated. In addition, records are a fragile thing, they are kept in special conditions. If such carriers in the collection look perfect, not damaged, then this indicates the owner of the thing as a very neat person.
What were and are
Records, like all sound carriers, are divided into types, depending on the material and properties. There are the following types:
- Hard records are thick, up to 3 mm, and rather heavy sound carriers. Very fragile and very finicky to play. They are called "gramophone" (method of reproduction) or "shellac" (material of manufacture).
- Flexible media. They have a capacity of up to 4 KB of data, where only 4 songs were placed, two per side. Their size is quite small and they were the closest in quality to CDs.
- Decorative plates and souvenirs. They were multi-colored, did not carry sound information as such, they were produced only as an element of the interior. Could be any shape.
- Handicraft plates were also made on thick films from X-rays. They called them a little with humor - "music on the ribs." These were unlicensed recordings of music.
Species and subspecies have accumulated quite a lot throughout the history of records. Now they produce mainly vinyl flexible products.
Gramophone records are one of the important pieces in historyhumanity. At that time, everyone was into them. Players were improved, it was prestigious and fashionable to have a library of records in those years. However, sooner or later everything becomes a thing of the past, so this popular sound carrier had to go down in history. Discs, flash cards and more have already replaced.
Today's youth prefer to listen to music directly via the Internet, which makes it very easy to find the right record. In addition, the available tracks are now much better quality than on gramophone records. Whether they will be revived is unknown. And is it worth it? There is no need to be nostalgic about the past fashion, every year the methods of transmitting sound and images are improving more and more, it is becoming easier to find the right melody or audiobook.
Recommended:
Electric musical instruments: description, principle of operation

Electronic musical instruments are devices used for sound synthesis purposes. The action is based on various electronic circuits. During the use of devices, it is possible to change the frequency, volume, duration of the sound of segments of compositions
M. A. Bulgakov, "The Master and Margarita": the genre of the work, the history of creation and features

Mikhail Bulgakov's novel "The Master and Margarita" received universal recognition, although this happened after the death of its author. The history of the creation of the work covers several decades - after all, when Bulgakov died, his wife continued his work, and it was she who achieved the publication of the novel. An unusual composition, bright characters and their difficult fates - all this made the novel interesting for any time
The gramophone is Definition, features, history and production

Some sophisticated music lovers prefer vinyl records to CDs. Why? This question should be asked directly to the musical gourmet. But the devices for playing these very records are extremely entertaining. Everyone has probably heard about gramophones, but the word "gramophone" causes indignation and absolute misunderstanding among many. Gramophone - what is it?
Michelangelo's "Creation of Adam" fresco. Description and history of creation
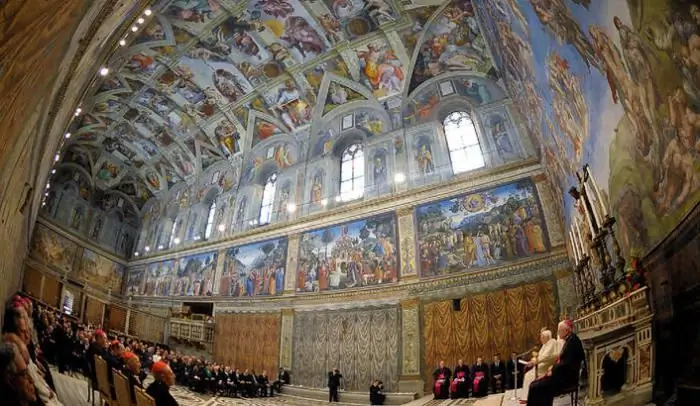

"The Creation of Adam" is one of 9 frescoes painted according to biblical scenes and making up the compositional center of the painting on the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel. Its author is Michelangelo Buonarroti (1475-1564)
Golden sequence: principle and features
Writing your own composition is extremely difficult. To do this, you need to be able to achieve harmonious sound. The golden sequence is one of the compositional techniques used in jazz and classical music. This method of obtaining harmonious sound was invented by the composer Handel

