2026 Author: Leah Sherlock | sherlock@quilt-patterns.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 17:46:27
Rhythm is the basis of musical literacy, the theory of this art form. In order to understand what rhythm is, how it is considered and how to follow it, it is important to be able to determine the duration of notes and pauses, without which even the most brilliant music would be a monotonous repetition of sounds devoid of emotions, shades and feelings. Let's consider this section of solfeggio in more detail, from the very beginning to the end.

Basic foundation of musical theory
Practically every person at one time or another studied music. Someone purposefully went to a music school, someone took private lessons from teachers. Most children receive basic knowledge in general education schools, where the teacher tells how to count to the music, beat with your hand to the beat, and pause. Therefore, almost everyone today understands what the duration of a note is, how this value can vary and what it depends on. Someone understood this better, others could not get into the shares at all. Therefore, if in childhood you had no problems with rhythm, and music lessons seemed to you an interesting and exciting pastime, then in this article you will find a lot of interesting things and, perhaps, discover a new talent in yourself. It is worth noting that this material can also become your textbook in the process of teaching a child music.

General concepts in this section
In order to make it clearer to every reader what it is and how it is applied in practice, and most importantly, how it interacts with music, we will consider the basic concepts and their meanings:
- Rhythm is the alternation of weak and strong beats that are inherent in every musical form. This is a kind of organization of sounds and their combinations.
- Size is the sequence of beats that divides any work into equal time intervals. These intervals we call shares.
- Tempo - the speed of the very beats that the metronome produces - the most commonly used device in music. With its help, the speed of performance of a particular piece is determined.
Note duration is a concept that contains all three of the above terms. Focusing on the type of note written in the book, you can determine its size. And now we come to the most interesting: what are the notes, what is the duration of each of them, how are they indicated on the letter and how to read them? Read the answers to all these and many other questions below.

Renderingmusic pictures
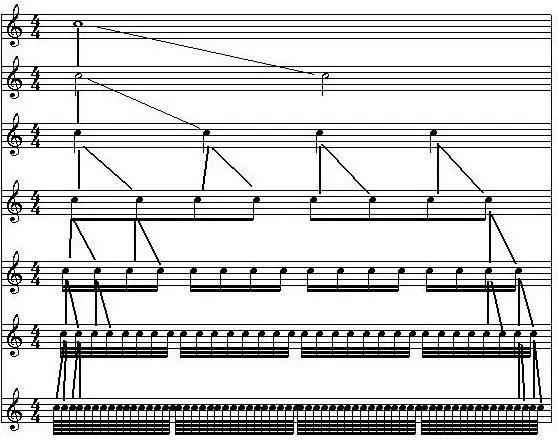
The first thing to understand when studying music is the division of the duration of sounds. The starting point for us is the duration of the whole note, since it is the longest sounding of the entire scale. A whole note is divided into halves, or half durations. In one whole note, there are two halves, which, in turn, are also divided in half, thus forming quarters, or quarter durations. It turns out that in one half note - two quarters, and in one whole - four. So such a division, a multiple of four, can occur indefinitely. Quarters are divided into eighths, those into sixteenths, then thirty-seconds, sixty-fourths, and so on. Based on this, we come to the conclusion that during the time that one whole note lasts, eight eighth notes or sixteen sixteenth durations can sound, which ultimately affects the virtuosity and technicality of a particular piece.

How to explain the duration of notes to a child
Such a scheme, of course, is understandable to every adult, but a child who is not familiar with mathematics, who does not yet have such a rich imagination and a large stock of knowledge, cannot comprehend it thoroughly. But there is a way that can get the kid to understand this part of music theory, and it's called - "dividing the pie." Imagine that we have a whole cake that has a certain weight. It is a whole note that lasts a certain amount of time. When we cut the pie in twohalves, their total weight does not change, and they occupy the same area. Half durations act as an analogy. Now we cut each of the halves in half, we get quarters. We get four quarters, each of which can be divided into two eighths. And next time, try to do it differently: cut the cake in half, divide one half into two more parts (quarters), and leave the other whole. So you will have a half and two quarters, that is, three parts, but one of them is large, and the other two are its halves.

Note duration and measure
All musical sounds, as you know, are combined into measures, the content of which, in turn, depends on the size. This indicator can have the following names: four quarters, two quarters, five quarters, and so on. It is the size that allows us to understand how to count the duration of the notes, how many different beats can be in a measure. It is customary to take one quarter as the basis of the size, which can be repeated two, three, four or more times. In the first case, it will be the size 2/4 (two quarters), 3/4, 4/4, 5/4 (five quarters - one of the most interesting and difficult to perform). If we choose, say, 4/4, this means that four quarters, or two halves, or one whole note can fit in one bar. Also there may be any other share combinations, which in total will represent four quarters. Less often in the works you can find the sizes, which are based on the eighth note. Most often the secondis a multiple of three, that is, we get the size 3/8 (three eighths), 6/8 and so on.

Designation of note durations
Now we come to how to decipher the printed note, how to determine its duration by its appearance. So, a given musical sign (we can say that it is the main one in this kind of art) always has a head, that is, a base. A calm can be attached to it, and a tail can be attached to a calm. How does this affect duration? So, a whole note, that is, the largest one, is a transparent (unshaded) semicircle without other details. Half durations are also not shaded, however, stems are assigned to them - sticks that are directed upwards (for those notes that are located in the lower part of the camp) or downwards (for higher sounds). The quarters also have a calm, but their heads are also completely shaded. We add a calm to the eights, a tail to the calm, and paint over the very base of the note. As for notes of shorter duration, they are all depicted as eighth notes, only they have double, triple, quadruple tails.
Rhythm, meter and tempo of music
As you have already understood, the duration of a note is the basis of the fundamentals, without understanding which it is impossible to further study and understand music. The technicality of any work depends on what lengths it consists of and at what speed they need to be played. It is by these indicators that professionals recognize the style of various classical composers. For example, it was typical for J. S. Bach to write more drawn-out works (althoughthere were also fairly fast ones), consisting of half and quarter parts, which should be performed at a slow pace. F. Chopin, on the other hand, wrote pieces consisting of eighths and sixteenths (often thirty-seconds), which were characterized by a very fast pace.
Recommended:
Is it possible to win the lottery? How to calculate lottery winnings? Probability of winning the lottery

Opinions about whether it is possible to win the lottery differ markedly. Some are firmly convinced that this is real, while others believe that there is no chance. Someone thinks that any game in the lottery is just money thrown to the wind, while others cite information about the numerous winnings of people from different parts of the world as counterarguments. Whom to listen to, whom to trust?
Notation for a beginner guitarist

From this article you will learn where the notes are located, what are tones and semitones, learn how to determine the size and beat of a piece, and you can also designate each guitar string
Litota. Examples will explain: reduction or simplification?

Litota is a trope. That is allegory in one form or another. If any thought needs to be conveyed to the interlocutor or reader not in its only meaning, but with an additional shade of meaning, and sometimes not with one, the trope is used
Guitar notes. Location of notes on the guitar

The article is intended for beginner guitarists who are interested in exactly how the notes are located on the guitar. It covers all the basic principles of the relative position of notes and how to detect them on a guitar fretboard
How to calculate odds on sports betting?

Bookmakers offer a huge number of bets on various sporting events. To make bets profitable, you need to understand how the odds are formed and how to correctly assess the probability of the desired outcome